使用SpinalHDL与cocotb完成经典交通灯控制器设计 需求分析
设计需求
十字路口东西、南北各有红、黄、绿指示灯,其中绿灯、黄灯和红灯的持续时间分别为 40s、5s 和 45s。对应状态机的四个状态
s0: 持续40s,东西绿灯亮,红灯和黄灯灭;南北绿灯和黄灯灭,红灯亮。
s1:持续5s,东西绿灯和红灯灭,黄灯亮;南北绿灯和黄灯灭,红灯亮。
s2:持续40s,东西绿灯和黄灯灭,红灯亮;南北绿灯亮,红灯和黄灯灭。
s3:持续5s,东西绿灯和黄灯灭,红灯亮;南北绿灯和红灯灭,黄灯亮。
添加检修功能,由单独的检修信号控制(开关量),从任何状态都可以进入检修状态,检修时间不定,但是检修结束后延迟5秒进入S0状态。
s4_0: 检修状态,红绿灯全部保持长亮,退出时开始启动定时器倒计时。
添加附加状态,通过触发信号控制,在正常工作状态下,一旦触发附加状态,当前状态会在结束后延迟30s再进入下一个状态(插入一个额外状态)。
s5_0: 保持30s,s0 -> s5_0 -> s1
s5_1: 保持30s,s1 -> s5_1 -> s2
s5_2: 保持30s,s2 -> s5_2 -> s3
s5_3: 保持30s,s3 -> s5_3 -> s0
设计分析
状态机采用两段式Moore状态机的设计,包括负责计算次态的组合逻辑、负责状态转移的时序逻辑以及负责输出的组合逻辑。
状态机转移条件主要基于时间,状态机控制一个计数器计数,节拍与计数器同步运行在1Hz的时钟域上。
倒计时输出采用2*8bit的无符号数输出。
交通灯控制输出采用2*3bit逻辑量输出。
附加状态具有延迟性,需要在当前状态结束时才进入,需要设计一个寄存器,用于缓存随时钟输入的附加状态控制信号。
总的时序逻辑资源为:
8Bit计数器
1Bit附加状态输入采样缓存
需要的外设
用于显示时间的数码管
用于模拟交通的LED输出
用于控制交通灯的按键
Verilog直接编写代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 module traffic_light_controller( input clk, input rstn, input sig_repair, input sig_pedestrian, output reg [2 :0 ] led_east_west, output reg [2 :0 ] led_north_south, output reg [7 :0 ] countdown_east_west, output reg [7 :0 ] countdown_north_south ); localparam st_s0_GR = 4'b0000 ; localparam st_s1_YR = 4'b0001 ; localparam st_s2_RG = 4'b0011 ; localparam st_s3_RY = 4'b0010 ; localparam st_repair = 4'b0110 ; localparam st_addition_0 = 4'b1000 ; localparam st_addition_1 = 4'b1001 ; localparam st_addition_2 = 4'b1011 ; localparam st_addition_3 = 4'b1010 ; reg [3 :0 ] st_cur, st_nxt; always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin if (rstn == 1'b0 ) begin st_cur <= st_s0_GR; end else begin st_cur <= st_nxt; end end assign st_addition = (st_cur == st_addition_0) || (st_cur == st_addition_1) || (st_cur == st_addition_2) || (st_cur == st_addition_3); reg sig_pedestrian_buf; always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin if (rstn == 1'b0 || st_addition == 1'b1 ) begin sig_pedestrian_buf <= 1'b0 ; end else if (sig_pedestrian == 1'b1 ) begin sig_pedestrian_buf <= 1'b1 ; end else begin sig_pedestrian_buf <= sig_pedestrian_buf; end end reg [7 :0 ] counter; always @(posedge clk or negedge rstn) begin if (rstn == 1'b0 ) begin counter <= 8'd40 ; end else if (st_cur ^ st_nxt) begin case (st_nxt) st_s0_GR, st_s2_RG: begin counter <= 8'd40 ; end st_s1_YR, st_s3_RY, st_repair: begin counter <= 8'd5 ; end st_addition_0, st_addition_1, st_addition_2, st_addition_3: begin counter <= 8'd30 ; end endcase end else begin case (st_cur) st_repair: begin if (sig_repair) begin counter <= 8'd5 ; end else begin counter <= counter - 1'b1 ; end end default : begin counter <= counter - 1'b1 ; end endcase end end always @(*) begin if (sig_repair == 1'b1 ) begin st_nxt <= st_repair; end else begin if (counter == 8'd1 ) begin case (st_cur) st_s0_GR: begin if (sig_pedestrian_buf == 1'b1 ) begin st_nxt <= st_addition_0; end else begin st_nxt <= st_s1_YR; end end st_s1_YR: begin if (sig_pedestrian_buf == 1'b1 ) begin st_nxt <= st_addition_1; end else begin st_nxt <= st_s2_RG; end end st_s2_RG: begin if (sig_pedestrian_buf == 1'b1 ) begin st_nxt <= st_addition_2; end else begin st_nxt <= st_s3_RY; end end st_s3_RY: begin if (sig_pedestrian_buf == 1'b1 ) begin st_nxt <= st_addition_3; end else begin st_nxt <= st_s0_GR; end end st_repair: begin st_nxt <= st_s0_GR; end st_addition_0: begin st_nxt <= st_s1_YR; end st_addition_1: begin st_nxt <= st_s2_RG; end st_addition_2: begin st_nxt <= st_s3_RY; end st_addition_3: begin st_nxt <= st_s0_GR; end default : begin st_nxt <= st_s0_GR; end endcase end else begin st_nxt <= st_cur; end end end always @(*) begin case (st_cur) st_s0_GR: begin led_east_west <= 3'b001 ; end st_s1_YR: begin led_east_west <= 3'b010 ; end st_s2_RG: begin led_east_west <= 3'b100 ; end st_s3_RY: begin led_east_west <= 3'b100 ; end default : led_east_west <= 3'b100 ; endcase end always @(*) begin case (st_cur) st_s0_GR: begin led_north_south <= 3'b100 ; end st_s1_YR: begin led_north_south <= 3'b100 ; end st_s2_RG: begin led_north_south <= 3'b001 ; end st_s3_RY: begin led_north_south <= 3'b010 ; end default : led_north_south <= 3'b100 ; endcase end always @(*) begin case (st_cur) st_s2_RG: countdown_east_west <= 8'd5 + counter; default : countdown_east_west <= counter; endcase end always @(*) begin case (st_cur) st_s0_GR: countdown_north_south <= 8'd5 + counter; default : countdown_north_south <= counter; endcase end endmodule
SpinalHDL程序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 class traffic_light_controller extends Component val io = new Bundle { val clk, rstn = in Bool () val sig_repair = in Bool () val sig_pedestrian = in Bool () val led_east_west, led_north_south = out Bits (3 bits) val countdown_east_west, countdown_north_south = out UInt (8 bits) } io.led_east_west := B "001" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := 40 io.countdown_north_south := 45 val coreClockComain = ClockDomain ( clock = io.clk, reset = io.rstn, config = ClockDomainConfig ( resetKind = ASYNC , resetActiveLevel = LOW ) ) val fsmArea = new ClockingArea (coreClockComain) { val sig_pedestrian_buf = Reg (Bool ()) init (False ) val fsm = new StateMachine { val counter = Reg (UInt (8 bits)) init (0 ) val s_0: State = new State with EntryPoint val s_1, s_2, s_3: State = new State val s_4: State = new State val s_5_0, s_5_1, s_5_2, s_5_3: State = new State s_0 .onEntry(counter := 40 ) .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "001" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := 5 + counter when(io.sig_repair) { goto(s_4) }.elsewhen(counter === 1 ){ when(sig_pedestrian_buf) { goto(s_5_0) }.otherwise { goto(s_1) } }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_1 .onEntry(counter := 5 ) .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "010" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(counter === 1 ) { when(sig_pedestrian_buf) { goto(s_5_1) }.otherwise { goto(s_2) } }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_2 .onEntry(counter := 40 ) .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "001" io.countdown_east_west := 5 + counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(counter === 1 ) { when(sig_pedestrian_buf) { goto(s_5_2) }.otherwise { goto(s_3) } }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_3 .onEntry(counter := 5 ) .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "010" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(counter === 1 ) { when(sig_pedestrian_buf) { goto(s_5_3) }.otherwise { goto(s_0) } }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_4 .onEntry(counter := 5 ) .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(counter === 1 ) { goto(s_0) }.otherwise { when(io.sig_repair) { counter := 5 }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } } s_5_0 .onEntry(counter := 30 ) .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(counter === 1 ) { goto(s_1) }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_5_1 .onEntry(counter := 30 ) .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(counter === 1 ) { goto(s_2) }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_5_2 .onEntry(counter := 30 ) .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(counter === 1 ) { goto(s_3) }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_5_3 .onEntry(counter := 30 ) .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(counter === 1 ) { goto(s_0) }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } } when(!sig_pedestrian_buf) { sig_pedestrian_buf := io.sig_pedestrian }.elsewhen(fsm.isActive(fsm.s_5_0) || fsm.isActive(fsm.s_5_1) || fsm.isActive(fsm.s_5_2) || fsm.isActive(fsm.s_5_3)) { sig_pedestrian_buf := False }.otherwise { sig_pedestrian_buf := sig_pedestrian_buf } } }
SpinalHDL与Verilog区别分析 状态机分析
SpinalHDL实现 利用SpinalHDL提供的fsm库,FSM与寄存器同属于时序逻辑,复位和时钟统一由其所属的时钟域管理配置(在创建时捕获对应的时钟域),FSM在StateMachine类创建的状态机中通过指定EntryPoint设定其首个状态,在编译结果中,SpinalHDL在复位后会默认到Boot状态,然后第一次时钟采样后进入对应的EntryPoint状态,保证首次进入状态是可以运行onEntry对应的状态初始化模块。如果不需要使用BOOT状态,可以使用makeInstantEntry()创建入口状态,这样可以失能Boot的生成。针对*1.*的EntryPoint、whenIsActive以及.onExit()其对应的Verilog实现对应如下:
onEntry : if (st_cur ^ st_next) case (st_next)
onExit : if (st_cur ^ st_next) case (st_cur)
whenIsActive : case (st_cur)
SpinalHDL的FSM可以自定义指定状态的编码,也可以指定编码方式自动编码(如独热码、格雷码)。
SpinalHDL 编译得到的Verilog程序中的两段/三段式状态机,但在Verilog程序中将不同功能集中在一个always语句块中,可读性较差。
寄存器分析
SpinalHDL的时序逻辑设计以寄存器对象为目标,寄存器在创建时捕捉对应的时钟域,寄存器的主要配置项目为其复位初值init(),以及何时采样何种信号。
直接通过寄存器的创建 接口就可以实现大多数功能
Reg(type : Data) init(),创建给定类型的寄存器,并可指定初值。RegNext(nextValue : Data),创建寄存器,该寄存器每个周期对输入的nextValue : Data进行采样,简单缓冲寄存器。RegNextWhen(nextValue : Data, cond : Bool, initData : Data),在满足条件cond时(时钟到达时)进行采样。实现更加复杂的流程,可以通过Reg创建寄存器,并自行设计赋值过程(采样目标)
端口的.setAsReg方法,可以直接将线缆/信号转换为寄存器。
仿真验证分析 cocotb仿真验证程序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 """ @Project :cocotb_study @File :runner_traffic_verilog.py @Author :PLMaple @Date :2024/11/28 17:29 @Brief : 交通灯控制器cocotb仿真测试程序 """ import randomimport cocotbfrom cocotb.clock import Clockfrom cocotb.triggers import Timer, FallingEdge@cocotb.test() async def main (dut ): dut.io_sig_repair.value = 0 dut.io_sig_pedestrian.value = 0 dut.io_rstn.value = 0 await Timer(1 , units='sec' ) dut.io_rstn.value = 1 clk_1hz = Clock(dut.io_clk, 1 , 'sec' ) await cocotb.start(clk_1hz.start()) for i in range (100 ): print_status_now(dut) await Timer(1 , units='sec' ) await FallingEdge(dut.io_clk) dut.io_sig_repair.value = 1 dut._log.info("-------------进入检修状态测试-20s-------------" ) for i in range (20 ): print_status_now(dut) await Timer(1 , units='sec' ) await FallingEdge(dut.io_clk) dut.io_sig_repair.value = 0 dut._log.info("-------------提出检修状态测试-20s-------------" ) for i in range (20 ): print_status_now(dut) await Timer(1 , units='sec' ) await Timer(random.randint(1 , 100 ), units='sec' ) await FallingEdge(dut.io_clk) dut.io_sig_pedestrian.value = 1 await FallingEdge(dut.io_clk) dut.io_sig_pedestrian.value = 0 dut._log.info("-------------附加状态测试-100s-------------" ) for i in range (100 ): print_status_now(dut) await Timer(1 , units='sec' ) def print_status_now (dut ): traffic_light = { 0 : "红" , 1 : "黄" , 2 : "绿" } led_east_west = dut.io_led_east_west.value.binstr led_north_south = dut.io_led_north_south.value.binstr color_1 = traffic_light[led_east_west.find("1" )] color_2 = traffic_light[led_north_south.find("1" )] dut._log.info( "东西方向:%s灯亮,倒计时:%ss,南北方向:%s灯亮,倒计时:%ss" , color_1, dut.io_countdown_east_west.value.integer, color_2, dut.io_countdown_north_south.value.integer, )
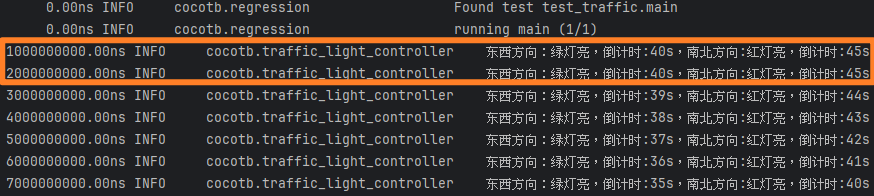
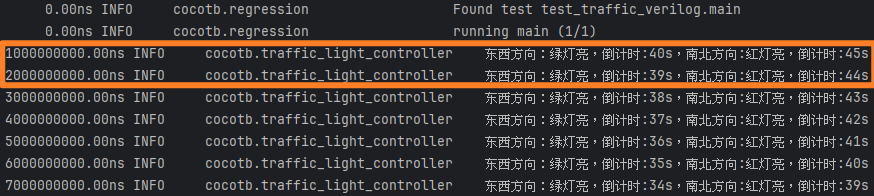
仿真结果 Verilog直接编写得到的交通灯控制器对应的i/o仅相差io_前缀,修改即可使用cocotb测试程序 对两种实现进行验证。Boot状态作为启动状态,导致SpinalHDL的启动慢于Verilog直接实现一个节拍。
SpinalHDL结果
Verilog结果
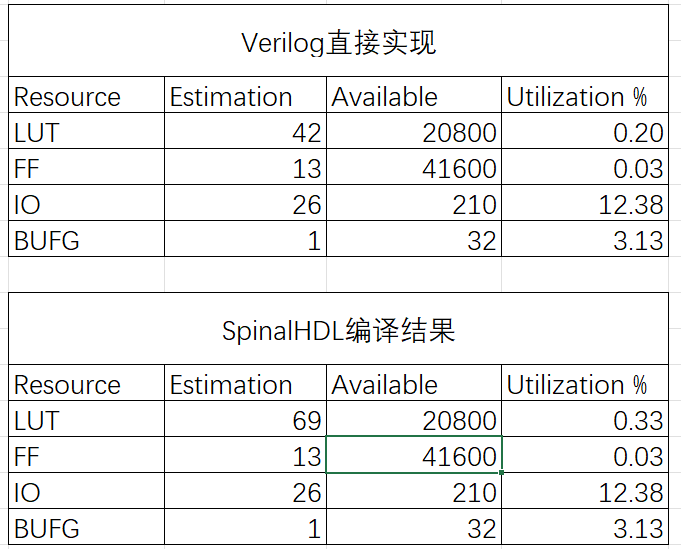
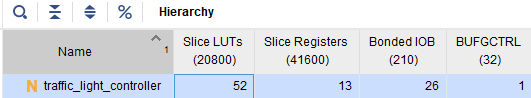
vivado综合结果 综合结果资源对比 使用到的触发器资源都为13个,与设计的8(公用计数器)+4(状态寄存器)+1(附加状态控制信号缓存)保持一致。二者的差异主要体现在LUT使用上,相比之下SpinalHDL额外使用了大量的LUT资源。
综合结果资源对比
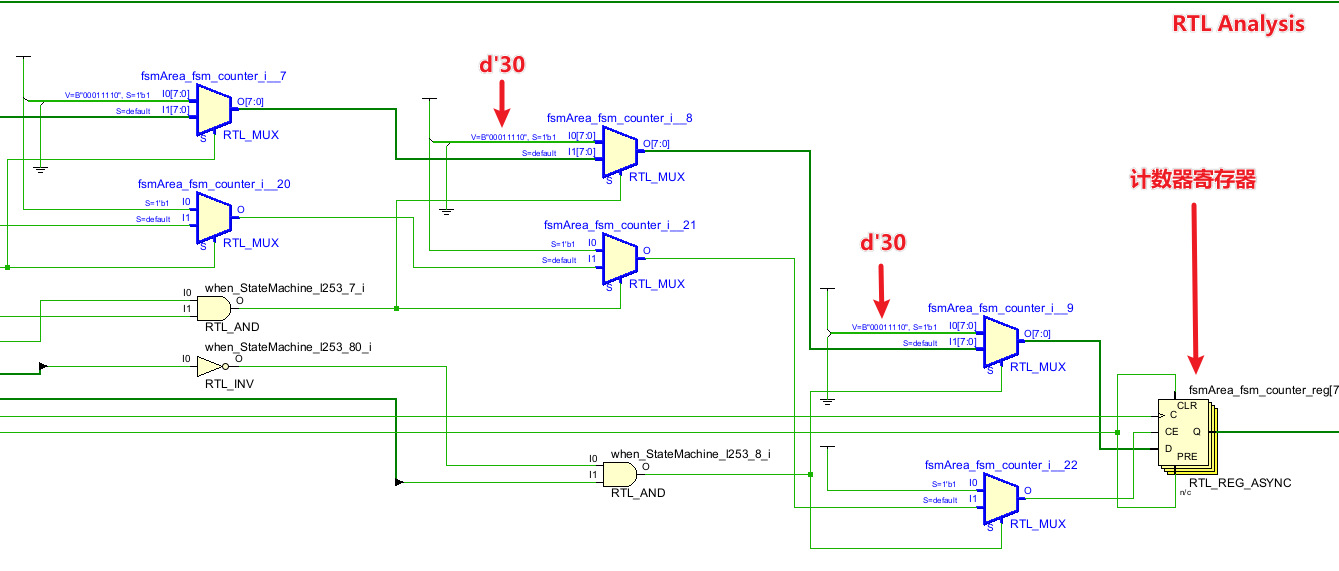
LUT资源分析 SpinalHDL编译生成的Verilog最明显的特征就是将所有的条件判断全部引入一个Wire,哪怕是相同的条件也不会进行复用,一个when就对应了一个条件,在RTL分析就可以看到对应的问题,哪怕是相同的赋值结果,也会分别被SpianlHDL生成的Verilog单独描述。
RTL Analysis
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 ssign when_trafficlightcontroller_l74 = (fsmArea_fsm_counter == 8'h01 ); assign when_trafficlightcontroller_l91 = (fsmArea_fsm_counter == 8'h01 );assign when_trafficlightcontroller_l108 = (fsmArea_fsm_counter == 8'h01 );assign when_trafficlightcontroller_l125 = (fsmArea_fsm_counter == 8'h01 );assign when_trafficlightcontroller_l142 = (fsmArea_fsm_counter == 8'h01 );assign when_trafficlightcontroller_l155 = (fsmArea_fsm_counter == 8'h01 );assign when_trafficlightcontroller_l168 = (fsmArea_fsm_counter == 8'h01 );assign when_trafficlightcontroller_l181 = (fsmArea_fsm_counter == 8'h01 );assign when_trafficlightcontroller_l57 = (fsmArea_fsm_counter == 8'h01 );assign when_StateMachine_l253 = ((! (fsmArea_fsm_stateReg == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_0)) && (fsmArea_fsm_stateNext == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_0));assign when_StateMachine_l253_1 = ((! (fsmArea_fsm_stateReg == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_1)) && (fsmArea_fsm_stateNext == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_1));assign when_StateMachine_l253_2 = ((! (fsmArea_fsm_stateReg == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_2)) && (fsmArea_fsm_stateNext == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_2));assign when_StateMachine_l253_3 = ((! (fsmArea_fsm_stateReg == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_3)) && (fsmArea_fsm_stateNext == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_3));assign when_StateMachine_l253_4 = ((! (fsmArea_fsm_stateReg == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_4)) && (fsmArea_fsm_stateNext == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_4));assign when_StateMachine_l253_5 = ((! (fsmArea_fsm_stateReg == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_5_0)) && (fsmArea_fsm_stateNext == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_5_0));assign when_StateMachine_l253_6 = ((! (fsmArea_fsm_stateReg == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_5_1)) && (fsmArea_fsm_stateNext == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_5_1));assign when_StateMachine_l253_7 = ((! (fsmArea_fsm_stateReg == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_5_2)) && (fsmArea_fsm_stateNext == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_5_2));assign when_StateMachine_l253_8 = ((! (fsmArea_fsm_stateReg == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_5_3)) && (fsmArea_fsm_stateNext == fsmArea_fsm_enumDef_s_5_3));
when_StateMachine_l253系列条件在Verilog直接实现中,可以直接通过异或和多路选择器进行表示,SpinalHDL Verilog的RTL分析没有任何复用,分别用一段单独的门电路实现,复用性极差,对条件进行复用整理(在SpinalHDL中为复杂的when条件创建对应的Bool变量,可以减少编译得到的Verilog文件中对条件的自动命名,同时可以极大程度地提高可读性),尝试降低LUT资源。解决条件复用问题后,Verilog可读性得到了一定程度地提高,复用定时器赋值后LUT资源得到了减少。
条件表达式优化后资源占用
优化后的SpinalHDL程序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 class traffic_light_controller extends Component val io = new Bundle { val clk, rstn = in Bool () val sig_repair = in Bool () val sig_pedestrian = in Bool () val led_east_west, led_north_south = out Bits (3 bits) val countdown_east_west, countdown_north_south = out UInt (8 bits) } val coreClockComain = ClockDomain ( clock = io.clk, reset = io.rstn, config = ClockDomainConfig ( resetKind = ASYNC , resetActiveLevel = LOW ) ) val fsmArea = new ClockingArea (coreClockComain) { val sig_pedestrian_buf = Reg (Bool ()) init (False ) val counter = Reg (UInt (8 bits)) init (40 ) val endOfCountdown:Bool = (counter === 1 ) val fsm = new StateMachine { val s_0 = makeInstantEntry() val s_1, s_2, s_3: State = new State val s_4: State = new State val s_5_0, s_5_1, s_5_2, s_5_3: State = new State setEncoding(graySequential) val entering_40s: Bool = isEntering(s_0) || isEntering(s_2) val entering_5s: Bool = isEntering(s_1) || isEntering(s_3) || isEntering(s_4) val entering_30s: Bool = isEntering(s_5_0) || isEntering(s_5_1) || isEntering(s_5_2) || isEntering(s_5_3) when(entering_40s) { counter := 40 }.elsewhen(entering_30s) { counter := 30 }.elsewhen(entering_5s) { counter := 5 }.otherwise { counter := counter } s_0 .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "001" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := 5 + counter when(io.sig_repair) { goto(s_4) }.elsewhen(endOfCountdown){ when(sig_pedestrian_buf) { goto(s_5_0) }.otherwise { goto(s_1) } }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_1 .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "010" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(endOfCountdown) { when(sig_pedestrian_buf) { goto(s_5_1) }.otherwise { goto(s_2) } }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_2 .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "001" io.countdown_east_west := 5 + counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(endOfCountdown) { when(sig_pedestrian_buf) { goto(s_5_2) }.otherwise { goto(s_3) } }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_3 .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "010" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(endOfCountdown) { when(sig_pedestrian_buf) { goto(s_5_3) }.otherwise { goto(s_0) } }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_4 .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(endOfCountdown) { goto(s_0) }.otherwise { when(io.sig_repair) { counter := 5 }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } } s_5_0 .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(endOfCountdown) { goto(s_1) }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_5_1 .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(endOfCountdown) { goto(s_2) }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_5_2 .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(endOfCountdown) { goto(s_3) }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } s_5_3 .whenIsActive { io.led_east_west := B "100" io.led_north_south := B "100" io.countdown_east_west := counter io.countdown_north_south := counter when(endOfCountdown) { goto(s_0) }.otherwise { counter := counter - 1 } } } val isAdditionState :Bool = fsm.isActive(fsm.s_5_0) || fsm.isActive(fsm.s_5_1) || fsm.isActive(fsm.s_5_2) || fsm.isActive(fsm.s_5_3) val sig_pedestrian_sample_en :Bool = !sig_pedestrian_buf when(isAdditionState) { sig_pedestrian_buf := False }.elsewhen(sig_pedestrian_sample_en) { sig_pedestrian_buf := io.sig_pedestrian }.otherwise { sig_pedestrian_buf := sig_pedestrian_buf } } }
总结
SpinalHDL具有充足的设计错误检查,编译结果可以避免非语义错误,结合仿真可以高效完成设计与验证。
SpinalHDL对总线和其他接口具有支持库。
SpinalHDL生成Verilog文件,可读性较差。
SpinalHDL本质还是硬件描述语言,通过适当的方法可以做到不引入额外的硬件开销,本次简单设计中,为了尝试SpinalHDL的硬件库而使用fsm库(状态机嵌套等复杂功能并未使用),导致了额外的资源开销,事实上,在SpinalHDL中完全可以一比一复制Verilog的实现思路,但相比Verilog也缺乏了一定的灵活性。
SpinalHDL中when(cond)使用的条件cond,如果涉及到复用的话,最好不要直接使用表达式,可以声明一个Bool量(对应Verilog的assign直接声明并赋值wire),可以提高Verilog程序的可读性。
参考资料
SpinalHDL中文文档1.0-时序逻辑-寄存器 SpinalHDL中文文档1.0-模块库-状态机 SpinalHDL FSM库的示例程序